
High-level design or HLD refers to the overall system, a design that consists description of the system architecture and design and is a generic system design that includes:
High-level design or HLD is also known as macro level designing .

What is High-Level Design
Important Topics for the High Level Design(HLD)
HLD document consists of data flows, flowcharts, and data structures to help developers in understanding and implement how the current system is being designed intentionally to function.
This document is responsible for:
HLD does not include physical requirements, port details, VLAN, and many other details.
The High-Level Design documentation presents the structure of the system as the application/database architecture, application flow, and technology architecture. High-Level Design documentation may use some non-technical terms, unlike low-level design which should be strictly technical jargon.
Note: Making the HLD is the responsibility of solution architects . After creating HLD, now expert experienced designers move towards LLD in accordance with the HLD’s criteria. LLD will provide details about how software entities will work whereas HLD focuses only on what software entities to place in an organization for efficient operation.
Here below constraints are expected from solution architects while designing HLD:
For providing a bird’s eye view of the entire solution, HLD should be possessing 2 elements as follows:
Illustration: Let us depict a high-level design via visual aid as shown below just to visualize the components and how the relationships are defined that is as follows:
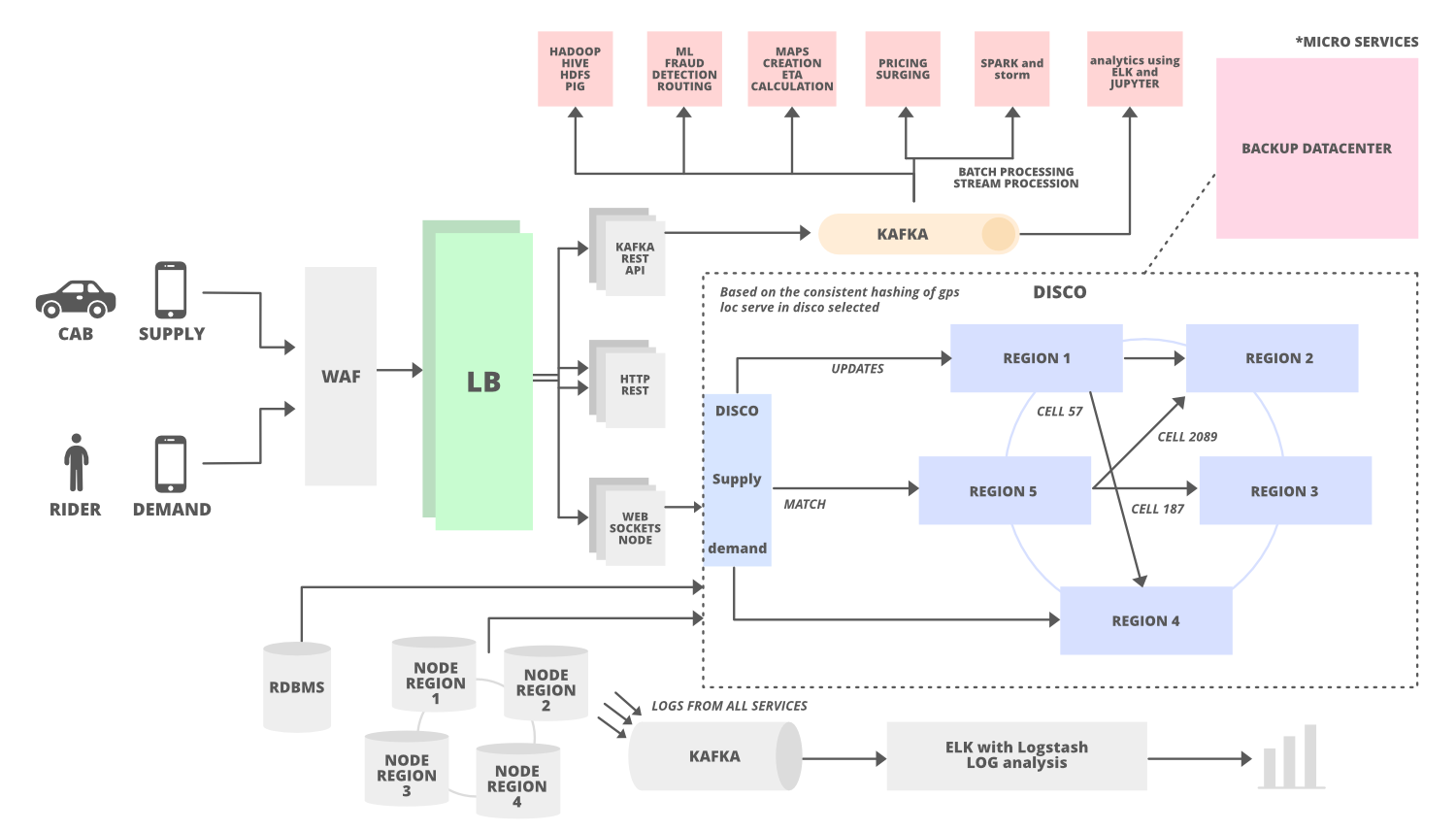
Components of High-Level Design
The purpose of this High-Level Design (HLD) is to add the necessary detailed description to represent a suitable model. This is designed to help with operational requirements and can be used as a reference manual for how the modules interact. Basically, HLD is a technical representation of functional requirements and the flow of information across assets or components.
| High-level Design | Low-level Design | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | HLD is the overall architect description of a system. | LLD is a designing module-level description of a system. |
| Designing process | Overall level design process. | Component-level design process. |
| Person involved | Solution architects | Designer and developers. |
| Conversion | Client requirements are being converted from a high-level design to as-per requirements. | Here it is been framed out for a detailed solution of the HLD. |
| Coding Involved. | No coding is involved in designing HLD. | Extremely detailed peculiar and specific code chunks snippets as per patterns are there while designing LLD. |
Let us now discuss the HLD roadmap after having an adequate understanding of HLD and how it is different from LLD which is shown below as an infographic:
Now in order to design any high-level system, certain terms are listed in a sequential manner so as to connect the dots in order to understand, Roadmap is very important for working professionals because these help us to get a complete binding understanding of how services in real-time are getting scaled at a high level.

How To Design Scalable High-level Design (HLD) Systems
Capacity estimation in system design involves predicting the resources (such as processing power, memory, and bandwidth) required to meet the expected workload. It ensures that a system can handle current and future demands efficiently, helping in the proper allocation of resources and preventing performance bottlenecks.
For example:
Twitter which is recently in newsfeeds these days, here at high-level designing we need to make sure tweets of popular influencers are reaching out to millions of people so how we need to scale our system so service should not be hampered.
We have also shown below the characteristics behavior of a server which is measured across throughput and latency within the system.

Comparison of Throughput and Latency with Concurrency : Behavior Of A Server
Tip: These are also important as per interview perceptive as constraint bounds in interviews in API over when to use what is very important.

In a client-server architecture , we are sending a request to server and server sends it back and so in this way communication takes place. But in designing the system biggest problem we face is whether we can implement the client-server model because we can not wait until the server responds.
Here Web Sockets play a crucial role that solving problems and enabling us to have real-time communication. They are more or less used in every system to be designed because we can not let our system wait for a response. They are very useful in Real-time web applications, gaming applications, chat applications.
Features of WebSocket are:

Polling is a technique of sending and receiving data from a server just likely as we do we doing above in the case of web sockets.
 Short polling vs long polling " width="1000" height="inherit" />
Short polling vs long polling " width="1000" height="inherit" />
Short polling vs long polling
In polling, we do have 2 types namely long polling and short polling.
Tip: Long polling is preferred over short polling because lesser number of requests are sent in a system.
Now before proceeding further think of what will happen to the server if there is no request thrown by clients. We keep hold of this while designing systems.
It is purposely built as one-way communication from servers to clients in specific design systems.
Example: Realtime streaming
.png)
The Control Room API supports filtering, pagination, and sorting for endpoints that return arrays of resources.
The filtering mechanism filters the required resources, the sorting mechanism places the resources in order, and the pagination mechanism then returns a specific range of those ordered resources. This topic provides you with the details to filter and sort the results of API requests and also guides you to handling the pagination of large result sets returned from an API request.
Note: Sorting and filtering are supported for substrings.
For example:
If you want to search for bots or files that have fin in their names, enter fin as the search criterion. All the bots and files that contain fin in the names will be displayed, for example, Finance, Finder, DeltaFinance, and Dolfin. Wildcards are not supported for searching and filtering bots or files.
Filtering allows you to apply Boolean conditions against a collection of returned resources in order to subset the collection to only those resources for which the condition is true. The most basic operation in Control Room API filters is to compare a field to a given value. It is possible to use equality comparison, range comparison, or logic. Use the following operators to compare a field to a constant value.
A rate limiter restricts the number of events that can be done in a timeframe by restricting the number of requests a sender can send in a given period of time. Here once the threshold limit is reached now further it blocks the incoming requests as can be seen below media as follows:
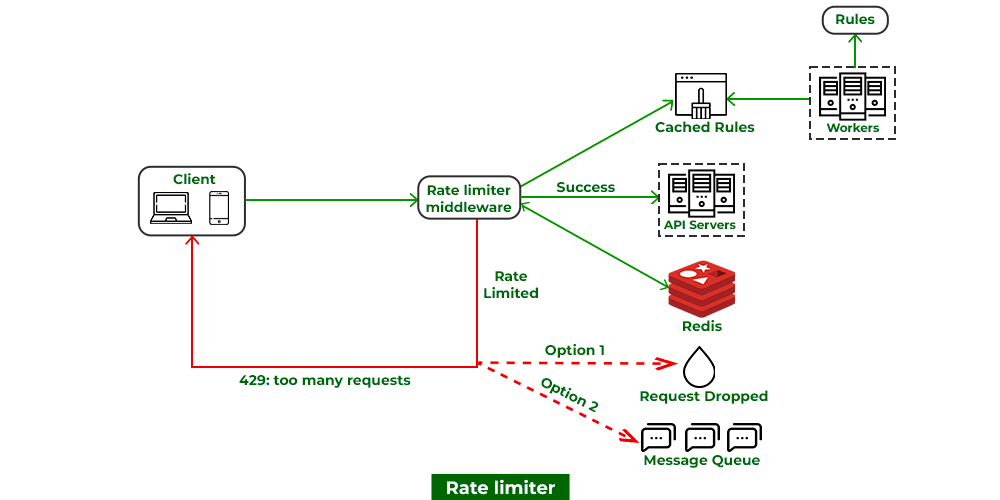
No matter how great a system we design there is always a chance of faults and failure tolerance which could be because of hardware issues or software issues(such as running low on memory) or there can be some human error. In such cases we need to provide resiliency via below means as follows:
Note: System design interviews starts with open ended designing a specific system which later is bounded with constraints at multiple levels. In order to clear dealing with these bounds in layman language is known as resiliency via implementing common tradeoff in the system. Hence providing resiliency is very crucial in designing complex system designs and also in clearing interviews.
As studied above at the HLD phase we are not bothered about the code but we are very peculiar about database designing at this level so we keep track of how data is going to Now this concept comes into play at last designing high-level systems where we can not. Filtering, as the name suggests we are filtering specific desired data from the database on basis of requirements such as geographical factors.
Apple company, pages out desired which will filter out specific products as per the geographical location.

A log file records details of events occurring in a software application. The details may consist of microservices, transactions, service actions, or anything helpful to debug the flow of an event in the system. Logging is crucial to monitor the application’s flow. This can also be useful for tracking the health and performance of a distributed system, as well as for debugging issues that may arise.
There are several approaches to implementing distributed logging, including: